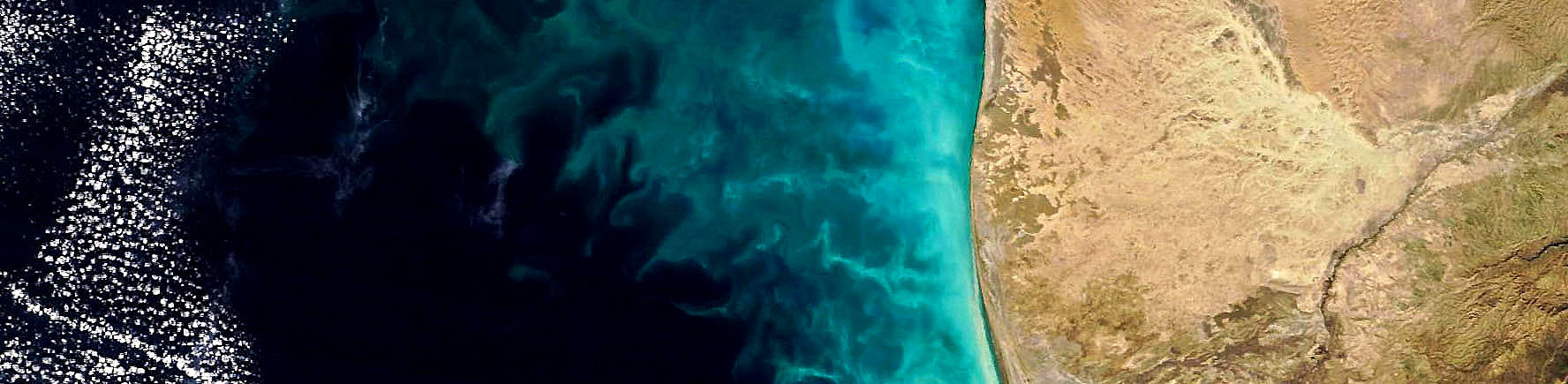The L1B values reported for each band/pixel are ’scaled integers’ (SI). These can be converted to radiance values using the band-dependent ’radiance_scales’ and radiance_offset’ values including in the hdf file. In tu the radiance can be converted to brightness temperature (top-of-atmosphere) using the Planck function. It is not possible to derive temperature from L1B radiances without knowing the emissivity of the observed object, or by performing inter-band comparisons. However, brightness temperature (the temperature for an ideal blackbody with the observed radiance) may be calculated from Planck’s Law, where
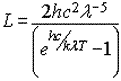 L = radiance (Watts/m2/steradian/m)
L = radiance (Watts/m2/steradian/m)
h = Planck’s constant (joule second)
c = speed of light in vacuum (m/s)
k = Boltzmann gas constant (joules/Kelvin)
λ = band or detector center wavelength (m)
T = temperature (Kelvin)
Inverting this formula to solve for temperature gives
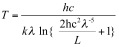
For a more precise conversion, you may wish to apply the filter response functions (aka Relative Spectral Response) to apply each detector’s wavelength response individually, and to weight the calculated temperature at each wavelength interval to get a centroid brightness temperature. To derive surface temperature you will also need to consider corrections for atmospheric contributions to the satellite-received signal.